
Science
Staff
Head of Science
Mr Michael McGovern
Head of Biology
Mrs Donna McCaffrey
Head of Chemistry
Mrs Mary O'Neill
Head of Physics
Miss Geraldine McAree
Subject Teachers
Mrs Donna McCaffrey
Mr Sean Carlin
Mr Ciaran McDonagh
Mr Brian Regan
Science Technicians
Mr Damian McAfee
The Science Department of St Michael's College is a large department comprising of eight Teachers each with their own modern and well-equipped laboratory.
All teachers are involved in the delivery of the Key Stage 3 Science curriculum to Years 8, 9, and 10. During these Years all classes have two double periods of Science weekly. At the end of Year 10 all pupils sit the Key Stage 3 exam in Science. The majority of pupils take the higher tier exam with a significant number achieving the higher levels of 7 and 8.

GCSE
In St. Michael's we offer Double Award Science at GCSE. Double Award Science as a subject has four key assessment components:
· Biology (two units)
· Physics (two units)
· Chemistry (two units)
· Controlled assessment of Practical Skills.
This subject is essential for entry onto the AS course in Biology, Physics and Chemistry and it is also desirable to have a good grade in this subject for entry onto the PE A-Level course.
Assessment Information
Students must complete six written examinations (two each in Biology, Chemistry and Physics).
Unit 1 exams (Year 11) for both Foundation and Higher Tier are each worth 11 percent of the final mark and last for 1 hour.
Unit 2 exams (Year 12) for both Tiers are each worth 14 percent of the final mark and last for 1 hour 15 minutes.
Controlled Assessment
In GCSE Double Award Science, 25 percent is awarded for the Practical Skills Unit.
Students must complete two controlled assessment tasks. They may attempt two or more tasks, up to a maximum of six. The two tasks must come from different subject areas in the specification.
Each controlled assessment task has three parts:
Part A – Planning and Risk Assessment
Students develop a hypothesis and plan an experiment to test it. They draw a blank table to record the results of their experiment, and carry out a risk assessment.
Part B – Data Collection
Students carry out the experiment and record the data collected in their results table.
Part C – Processing, Analysis and Evaluation
Students answer questions relating to their own work, demonstrating scientific knowledge and understanding. They also show their ability to process, analyse and evaluate information they have collected from their experiment.
After Year 12 many boys choose to continue with Science, by taking an AS/A level in one or more of the Sciences. These are taught individually by the specialist teachers.
A Level
- Examing Board: CCEA
Biology
Biology is concerned with the internal physiology of animals and plants and is an extremely diverse subject crossing over into areas such as biochemistry and nanotechnology. Biology is a desirable, and often essential, subject for many third level university courses including medicine, dentistry, biology, food science, agricultural science and the many medical related courses such as radiology, physiotherapy, speech therapy and nursing. Biology is a popular A-Level. Approximately 40 pupils per year take Biology.

Careers
Careers associated with A-Level Biology include:
-
Pharmacy
-
Medicine
-
Dentistry
-
Physiotherapy
-
food technology
-
food science
-
dietetics
-
nutrition
-
radiology
-
speech therapy
-
nursing
-
teaching
and the huge number of research opportunities that arise in biochemistry, biotechnology, nanotechnology, genetics, microbiology.
There are numerous career opportunities in the area of the environment such as environmental officers, land management, pollution monitoring and new green technologies.
Physics
- Examing Board: CCEA
Subject Introduction
Physics is currently offered as a component of Double Award Science and Applied Science at GCSE Level and at AS and A2 Level. A Level Physics is a popular choice at St. Michael’s. The course specification is designed to promote continuity, coherence and progression within the study of Physics. The AS course builds on the knowledge, understanding and skills developed at GCSE level. A2 builds on the foundations provided by AS. The subject is theoretical and practical and demands a high level of commitment by students. A level Physics students need to have good mathematical skills.
Qualification & Specification details
The full Advanced GCE A level award is based on students’ marks from the AS (40 %) and the A2 (60 %).

Careers
The specification promotes continuity, coherence and progression within the study of physics. The A Level award provides a basis for further study at tertiary level of physics, electronics and engineering. For those progressing directly into employment, an AS or A Level award is relevant not only in the fields of science, engineering and medicine, but also to areas of commerce and public service that value problem-solving and practical skills. The specification helps to provide an understanding of the impact of technological developments on the environment.
Physics is the route to many career options, for some ideas take a look at the following web sites :
Advanced GCE (A2) consists of three modules:
A2 Module 1 Deformation of Solids, Thermal Physics, Circular Motion, Oscillations and Atomic
and Nuclear Physics
Externally assessed Written paper – 2 hours
24% of A Level
A2 Module 2 Fields, Capacitors and Particle Physics
Externally assessed written paper – 2 hours
24% of A Level
A2 Module 3 Practical Techniques and Data Analysis
2 components (1 hour each)
-
Externally assessed test of practical skills
-
Written paper – analysis of experimental results
12% of A Level
Chemistry
- Examing Board: CCEA
Chemistry is the study of elements and the compounds they form. The spiritual, moral, ethical, social and cultural issues arising from such study enables students to discuss and analyse Chemistry’s contribution to society.
This involves:
• A critical appraisal of the use of finite resources and the way in which they are used;
• Development of a global responsibility for ethical use of advances in Chemistry.
This specification contributes to environmental education by indicating ways in which Chemistry impinges on our environment. Students become aware of environmental and health and safety considerations through the following course content:
• Hydrocarbons
• Alcohols
• Equilibrium
• Kinetics
• Transition metals.
Questions using stimulus material exemplify European developments in environmental
and health and safety considerations.
Qualification & Specification details
The full Advanced GCE A level award is based on students’ marks from the AS (40 %) and the A2 (60 %).
The full Advanced GCE A level award is based on students’ marks from the AS (40 %) and the A2 (60 %).

Careers
Apart from being a chemist, chemistry opens the door to many careers. For some it is an essential requirement; medicine, pharmacy, veterinary, dentistry, chemical engineering and chemistry, but for many others it is an advantage; agriculture and food science, biochemistry, forensic science, materials scientist, metallurgist, research and teaching. It is a requirement for one of the most innovative science based degrees in the UK at present, BSc Stratified Medicine at Ulster University, Coleraine.
The CCEA GCE Life and Health Sciences
- Examing Board: CCEA
The CCEA GCE Life and Health Sciences specification was developed with industry in response to the needs of the growing life and health sciences sector in Northern Ireland.
Life and health science related industries make up over 25% of Northern Ireland’s total economic output and include a diverse range of public and private businesses and employment opportunities, including pharmaceutical, chemical, agricultural, dental, nursing, environmental and allied health professions.
This specification is available at two levels: AS and A2 (Single and Double Award). Students can take the AS units plus the A2 units for a full GCE A level qualification. They can also choose to take the AS course as a stand-alone qualification.
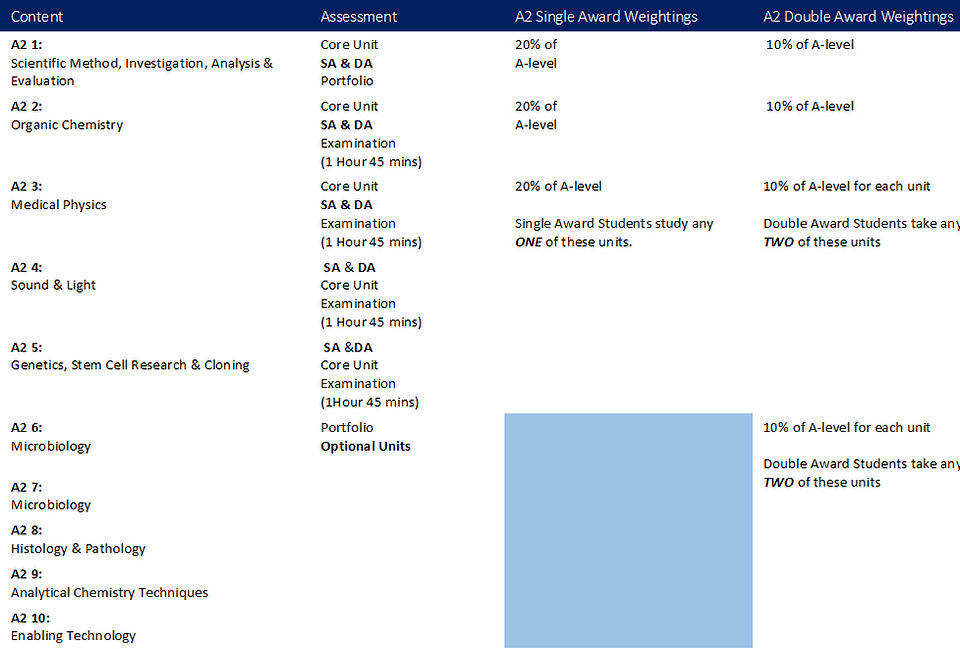
For a full GCE Single Award qualification students must complete six units: three at AS level and three at A2.
For a full GCE Double Award qualification 12 units are required: six at AS level and six at A2.
The specification has 16 available units. Some units are compulsory (C) while others are optional units (O).
-
Unit AS 1: Experimental Techniques
-
Unit AS 2: Human Body Systems
-
Unit AS 3: Aspects of Physical Chemistry in Industrial Processes
-
Unit AS 4: Brain Science
-
Unit AS 5: Material Science
-
Unit AS 6: Medicine, Drugs and Clinical Trials
-
Unit A2 1: Scientific Method, Investigation, Analysis and Evaluation
-
Unit A2 2: Organic Chemistry
-
Unit A2 3: Medical Physics
-
Unit A2 4: Sound and Light
-
Unit A2 5: Genetics, Stem Cell Research and Cloning
-
Unit A2 6: Microbiology
-
Unit A2 7: Oral Health and Dentistry
-
Unit A2 8: Histology and Pathology
-
Unit A2 9: Analytical Chemistry Techniques
-
Unit A2 10: Enabling Technology.
What do you need to study Life and Health Sciences?
You need to have a real interest and ability in the sciences.
Career Opportunities
Northern Ireland has a thriving life and health sciences sector that benefits from a strong collaborative approach between industry, academia, and clinicians. The region offers expertise across precision medicine, clinical trials, and digital health. Northern Ireland also has clinical specialisms within the areas of oncology, cardiology, ophthalmology, respiratory and diabetes. 13,000 people study life and health sciences related subjects at university. The Life and Health Sciences aims to develop students’ advanced practical skills and knowledge, preparing them for employment or third level study and a career in the life and health sciences.
AS Single Award (SA) & Double Award (DA) Specification at a Glance
%20%26%20Double%20Award%20(DA)%20Specification%20at%20a%20Glance.jpg)
A2 Single Award (SA) & Double Award (DA) Specification at a Glance
%20%26%20Double%20Award%20(DA)%20Specification%20at%20a%20Glance.jpg)






